Research Facilities
Research Facilities and Innovation Campuses
In state-of-the-art facilities across the state, Clemson researchers are utilizing advanced technology to create a safer, healthier and more sustainable future.
Research Facilities
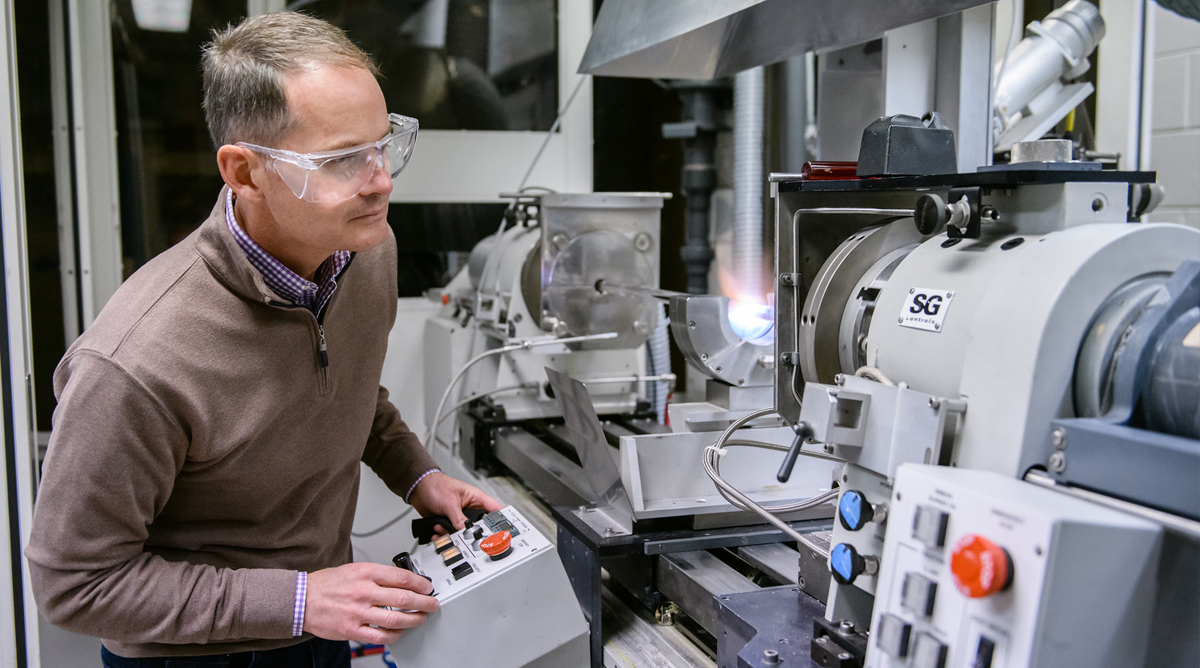

COMSET
Center for Optical Materials Science and Engineering Technologies was formed in 2000. COMSET provides an organized framework with a significant centralized infrastructure for faculty with common interests to collaborate in developing advanced materials, devices, and systems that generate, transmit, manipulate and utilize light. The science and engineering of light-based technologies is approaching a $7.5 trillion dollar global market. With materials as the technology enabler within all devices and components, Clemson University and South Carolina, through COMSET, are uniquely positioned to support the research, workforce development, and outreach needs of the industry.
COMSET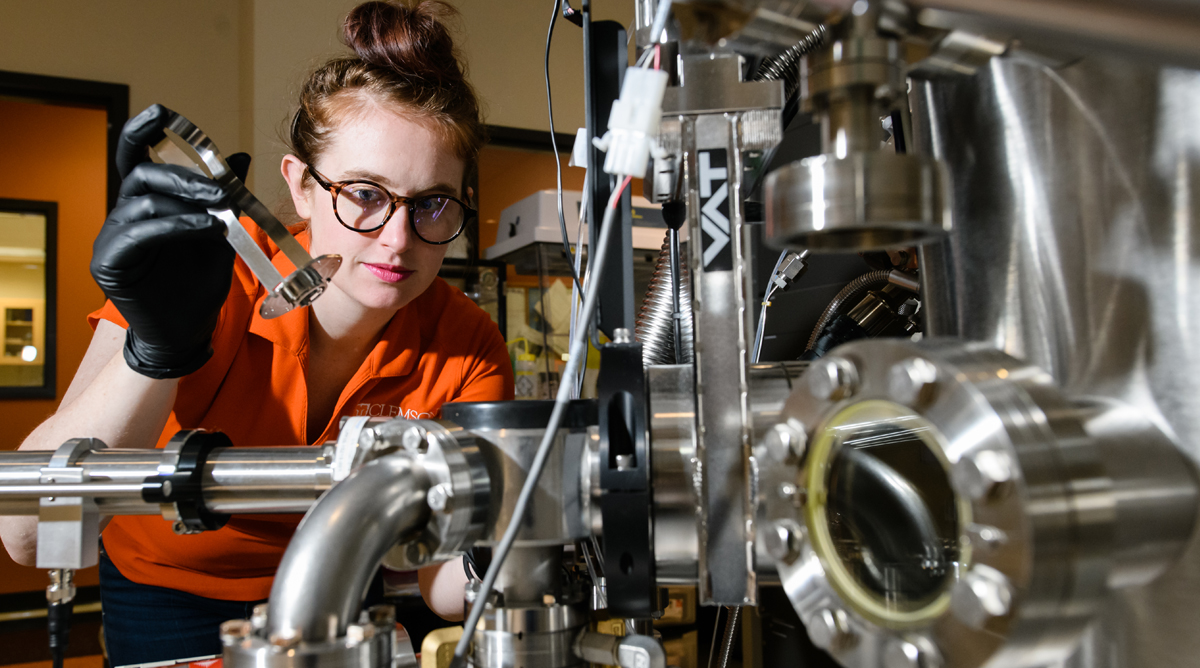
Electron Microscopy
Electron Microscopy Facility has several state-of-art high-resolution transmission electron microscopes, scanning electron microscopes, and a combined Focused Ion Beam microscope. Our goal is to provide the best microscopy and analytical services to our faculty and industrial collaborators. The multi-use facility, located 3.5 miles north of I-85 on SC 187 in Anderson, attracts clients from aerospace, automotive, pharmaceutical, textile, electronics, environmental and medical industries. To use the instrumentation, email a facility staff member who will coordinate one-on-one training and then facilitate your registration on an online scheduling platform.
EM Lab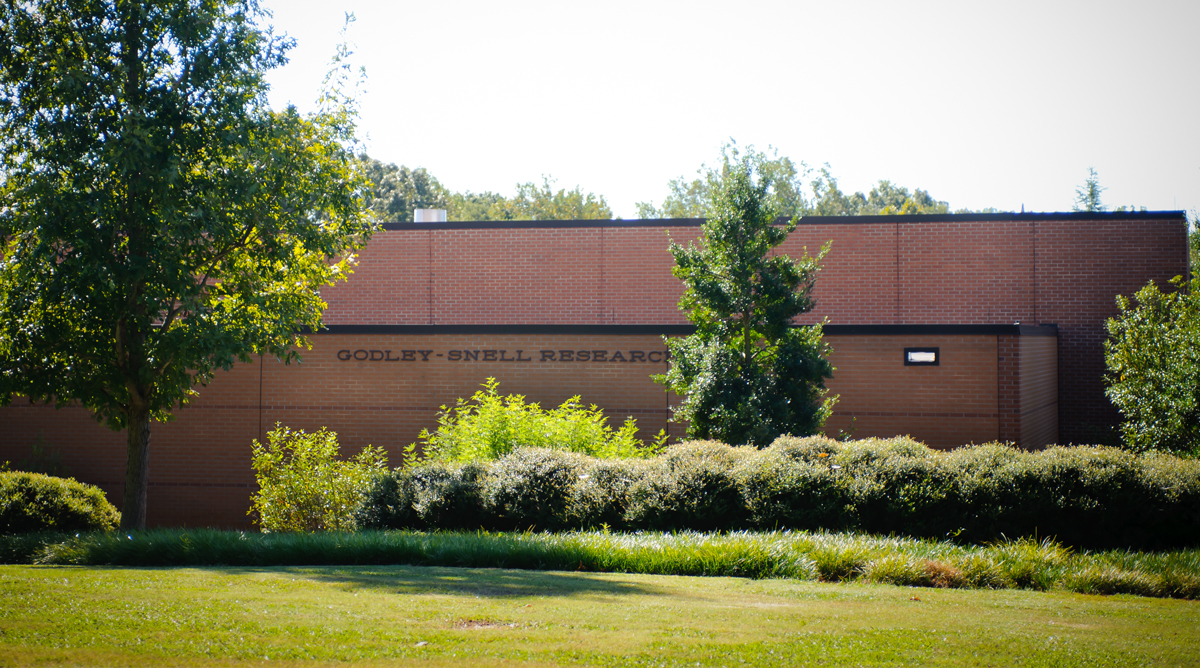
Godley-Snell Research Center
The Godley-Snell Research Center (GSRC), located on the Clemson University main campus, is a centralized animal research facility with 22,000 sq. ft. dedicated to maintaining a variety of laboratory animal species used in research and teaching programs at Clemson University, and to provide resources and support services for those programs. Animal welfare is managed by the Office of Animal Services. Environmental parameters are monitored continuously using a computer-controlled monitoring system with dial-out alarms. The surgical facility has two large operating rooms, a nursing station, sterile prep, recovery room, procedure, and surgical prep room, and radiology.
GSRC
IBIOE
The Institute for Biological Interfaces of Engineering (IBIOE) is a South Carolina-based interdisciplinary research and educational unit, spanning each of the Clemson University colleges. Our mission is to develop state-of-the-art systems for solving practical and clinically relevant problems through strategic interdisciplinary research partnerships and unique educational initiatives. Lab capabilities include fabrication, mechanical testing, chemical detection, gene/protein detection, cell culture test equipment, and cell culture equipment. Focus areas are advanced biomaterials, tissue fabrication and instrumentation, and tissue simulation.
IBIOE
National Brick Research Center
The National Brick Research Center is an industrially funded organization providing research, education, and service to producers and users of clay bricks and other ceramic materials (tile, mortar, and ceramics). Entities join the Center by paying annual dues according to a schedule set by the Center’s Industrial Board of Directors. The Center seeks to augment the university students' educational process and be an important contributor to the University’s mission in research and public service. Educational Services: including Short courses, Webinars, Brickyard Magazine, and Annual Brick Forums are available.
NBRC
Palmetto Cluster
Palmetto Cluster is a “condominium” style cluster developed to serve the university’s wide-ranging research needs. Designed and deployed by Clemson Computing and Information Technology's Advanced Cyberinfrastructure (ACI) group in collaboration with faculty researchers across the university, Palmetto provides a shared platform that optimizes resources for the benefit of all users. Named for South Carolina’s state tree, the Palmetto Cluster was designed to suit many different research applications, with a large number of powerful multi-core nodes, each with a significant amount of memory.
Palmetto ClusterInnovation Campuses

Advanced Materials Research Lab

Biomedical Engineering Innovation Center
Clemson University Biomedical Engineering Innovation Center (CUBEInc) is a state-of-the-art facility primarily dedicated to biomedical research and accelerated innovation. CUBEInC consists of 30,000 sq. ft. of research and education facilities, translational/incubator space, bioimaging research facilities, state-of-the-art surgical-skills facilities, as well as meeting and networking accommodations shared by Clemson scientists and GHS clinicians. CUBEInC occupies the 4th floor of Building C of the Patewood Medical Campus of the Greenville Health System (GHS). It is strategically located above two floors dedicated to clinical orthopedics and rehabilitation (sports and total-joint replacements) and one floor dedicated to vascular surgery and clinical imaging.
CUBEInc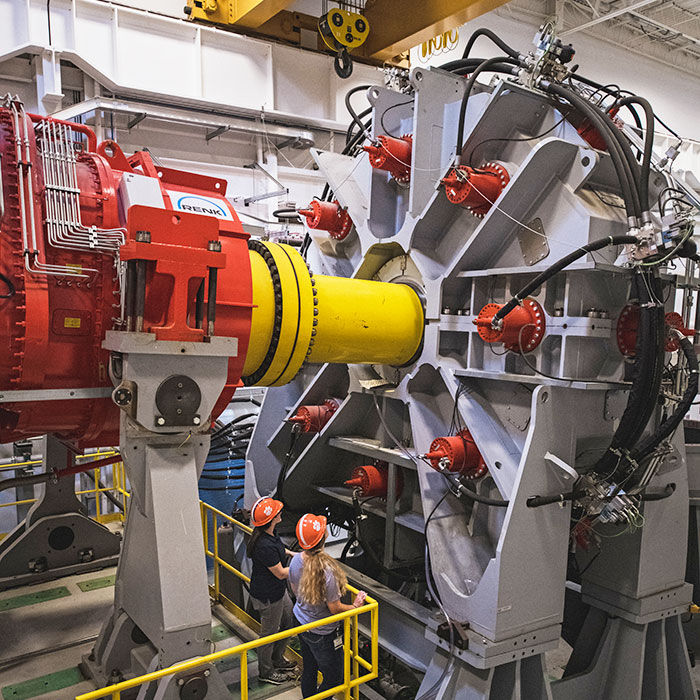
Clemson University Restoration Institute
Clemson University Restoration Institute (CURI) was established in 2004, in North Charleston, as a means for driving economic growth, innovation, and workforce development in South Carolina's Lowcountry. Facilities in North Charleston provide researchers, scientists, students, and faculty with ample opportunity to impact the growing tech economy while also appreciating the rich historical heritage in the surrounding area. At any given time, teams can be found working on a diverse range of projects including historic preservation, restoration ecology, advanced materials research, digital production arts and filmmaking, marine conservation, and electric grid testing.
CURI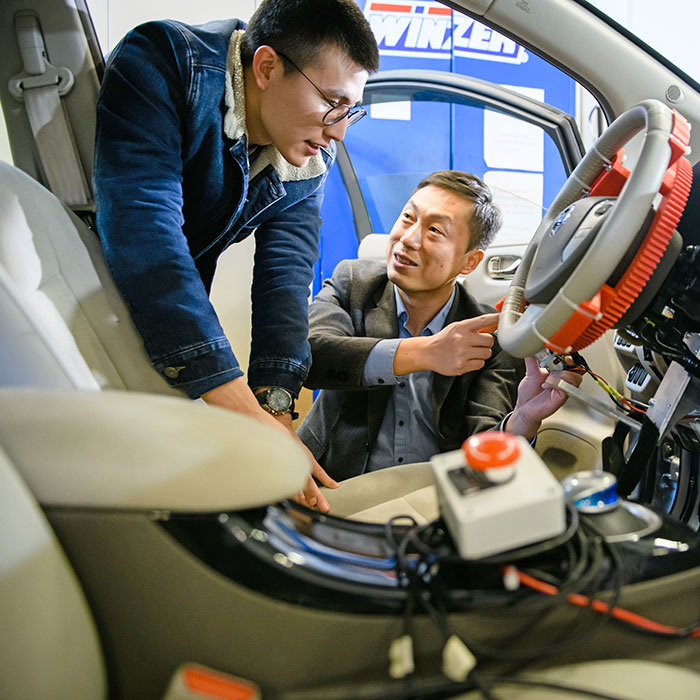
Clemson University International Center for Automotive Research
Clemson University International Center for Automotive Research (CUICAR) is an advanced-technology research campus where education, research, and economic development collaborate to create a global venue for the automotive industry. CU-ICAR’s research portfolio is driven by industry needs. It continuously analyzes the market and surveys industry partners, industry leaders, and automotive companies to determine their technology and R&D focus. Beyond housing 17 resident partners, multiple research laboratories, and Clemson University’s automotive engineering program, the CU-ICAR campus also lends itself to accommodating regional and global conferences and events.
CUICAR